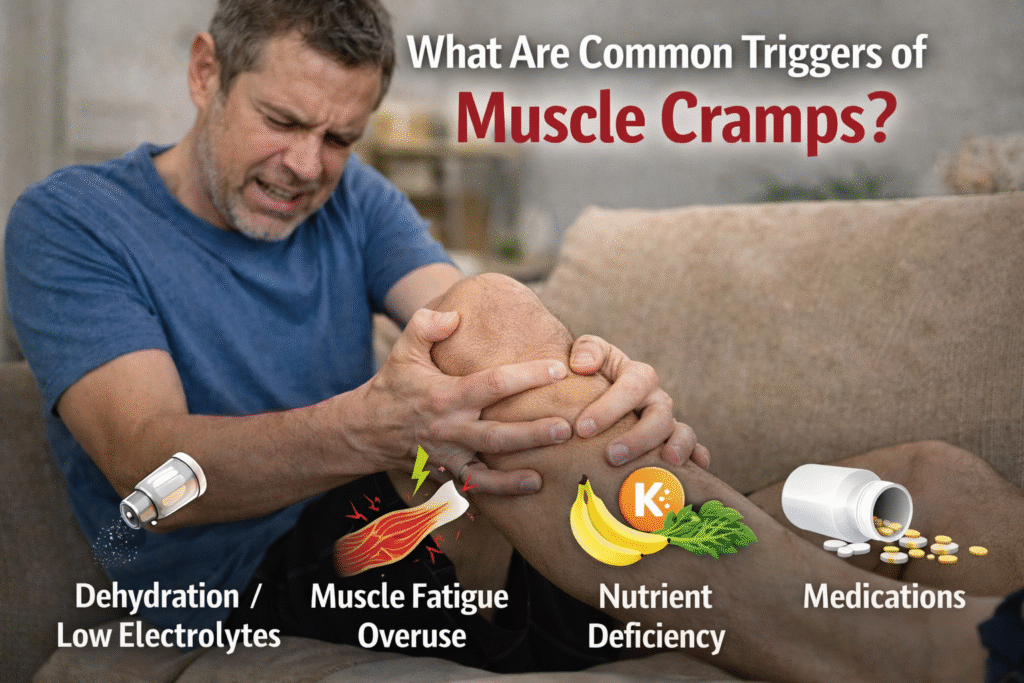
Common triggers of muscle cramps are dehydration, imbalances of electrolytes, overuse of the muscles, lack of proper circulation, sitting or standing in one position, and some medical conditions and drugs. Muscle cramps can be described as the involuntary contraction of the muscles. Which can not be relaxed and are usually followed by sudden pain and tightness.
At Sahara West Urgent Care & Wellness, we frequently treat adults in Las Vegas who experience muscle cramps related to heat exposure, dehydration, and physical activity.
Muscle Cramps: What Triggers
Dehydration
Dehydration is among the major causes of muscle cramps. In case the body lacks sufficient fluid, muscles are denied sufficient oxygen and nutrients and thus, they would contract involuntarily.
Fluid loss also makes the blood thick and this pulls down the blood circulation to the working muscles further putting pressure on painful spasms. It is particularly prevalent when a person is ill, during physical activity or when he or she is long exposed to heat.
Dehydration can happen very fast in hot and dry climates such as Las Vegas and even without physical activity, thus causing more frequent muscle cramps in adults who fail to replace fluids on a regular basis.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium are important electrolytes that are important in muscle contraction and relaxation. These are the minerals, which facilitate the passage of electrical messages between muscles and nerves.
In the case of electrolyte imbalance, which is caused by excess sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, improper diet, or some drugs, the muscles may contract irregularly, resulting in cramping.
The following are common in people who have electrolyte imbalances:
- Vigorous physical activity without a deficit.
- Work outdoors
- Consume excessive alcohol
- Are recovering from illness
Muscle Overuse or Strain
Cramps of the muscles are normal following overwork or strain of the muscles. Monotonous motor activities, standing on the legs too long or vigorous muscle activities may exhaust muscle fibers, which can easily develop spasms.
Inadequacy in warm up, stretching or recovery period also adds to the risk. Overuse cramps are common in:
- Athletes
- Outdoor workers
- People who begin with new exercise programs.
Poor Blood Circulation
Adequate blood circulation in the body is required to pass oxygen and nutrients to the muscles. Muscle cramps, especially of the legs, can be provoked by reduced circulation, which occurs due to long sitting or standing, tight muscles, or vascular disease.
Individuals who experience circulation problems may experience cramps during exercise or when they are sleeping. The bad circulation may also aggravate cramps brought about by dehydration or loss of electrolytes.
Prolonged immobility or Awkward Postures
Spending most of the time in the same position, like sitting in front of a desk or driving long distances or sneezing in awkward positions, may limit the blood circulation and cause nerves to become squashed.
This may lead to spasms or cramps occurring suddenly on muscles particularly in the calves, feet or the hands.
Medical Conditions
Some diseases predispose to cramps of the muscles in some way. These include:
- Diabetes that is likely to harm nerves and circulatory systems.
- Kidney disease, which is a condition of fluid and electrolyte control.
- Thyroid disorders affecting the metabolism of the muscle.
- The compression of nerve or conditions in the spine, which interrupt nerve signals.
In case the muscle cramps are common, severe or increasing, it is worth seeking medical attention to eliminate other underlying conditions.
Medications
Certain drugs may predispose people to cramping through a change in fluid or electrolyte balance or muscle activity. Common examples include:
- Diuretics, fluid loss, is increased.
- Statins, potentially of muscle effect.
- Meditations that can affect circulation include blood pressure drugs.
In case cramps start with the appearance of some new medicine, it is better to contact a healthcare professional.
What are the symptoms of muscle spasms (muscle cramps)?
Muscle spasms may range between mild to severe. In mild cases, a muscle can get the impression that it is twitching or moving spontaneously and the movement can be seen through the skin. In more severe forms, the muscle can suddenly contract itself into a hard painful knot, otherwise known as a cramp. This is mostly typical of the legs.
Should a muscle spasm be severe, pain or tenderness on the affected part may linger on the affected part hours or even one or two days later after the spasm has disappeared.
In cases where the underlying neurological condition causes muscle spasms, there are other symptoms that may arise and these include:
- Muscle pain
- Muscle weakness
- Paralysis
- Numbness or tingling
- Poor coordination
- Difficulty sleeping
- Vision problems
Who gets muscle spasms?
Spasms in muscles can happen to anybody and can happen any time either when one is walking, sitting, exercising or even sleeping. Others are more susceptible to muscle spasms and can have them quite often, particularly following or preceding physical exercises.
Individuals who are at risk of muscle spasms include:
- Athletes
- Infants
- Pregnant women
- Adults over the age of 65
- People with obesity
Risk factors of Muscle Cramps
Some of the causes that may predispose one to muscle cramps are:
- Age: As individuals age, their muscles reduce in size and this increases fatigue and damages of the muscle.
- Lack of proper physical conditioning: Muscles that lack proper conditioning wear out easily exposing them to the possibility of spasms.
- Gross sweating: During the hot weather, heavy sweat, particularly in physical activities, may cause the loss of fluids and electrolytes which would cause muscle cramps.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women are more likely to experience muscle cramps mostly at the legs.
- Health conditions: Medical conditions like diabetes, disorders of the nerves, liver or thyroid may also increase the risk.
- Excess body weight: It has been found that being overweight or obese is an added burden on the muscles making cramps more prone to occur.
The reason behind the muscle cramps in Las Vegas
The arid climate of the desert in Las Vegas predisposes individuals to dehydration and the loss of electrolytes, which makes muscle cramps more frequent, in particular, during hotter seasons or when an individual exercises or works outside or engages in physical activity and has alcohol.
Should You Seek Urgent Care over Muscle Cramps?
You are supposed to go to the urgent care in case of muscle cramps:
- Are severe or persistent
- Availability, without apparent cause.
- Companied with swelling, weakness, numbness, or confusion.
- Not sensitive to hydration or rest.
- Take place following illness, vomiting or diarrhea.
Sahara West Urgent Care & Wellness in Las Vegas offers same-day assessment, IV therapy, and electrolyte therapy to this patient to ensure he/she is treated of the underlying cause and to help alleviate the muscle cramps.
Treatment of Muscle Cramps in The Urgent Care
Treatment may include:
- Vital signs observation and medical examination.
- IV fluids therapy and electrolytes replacement.
- Muscle relaxants (where necessary)
- Management of co-morbidities.
A significant number of patients feel relieved immediately after treatment.
How to Prevent Muscle Cramps
To reduce your risk:
- Keep yourself well hydrated all day long.
- Replacement of electrolytes during exercise or in the heat.
- Warm up and cool down of physical activity.
- Avoid prolonged inactivity
- Maintain a balanced diet
Las Vegas, Nevada Walk-In Care of Muscle Cramps
It is time to see Sahara West Urgent Care & Wellness in case the muscle cramps are disrupting your day-to-day life or not getting better with homemade treatment.
- West Sahara Ave, Las Vegas
- Walk-ins are always welcome. Same-day care is available.
- IV hydration and acute care services.
To schedule your appointment with the highest standard of care, visit Sahara West Urgent Care on our website, where you can also explore more informative blogs .
FAQs
What is the difference between a muscle cramp and a muscle spasm?
A muscle cramp is a sudden, painful, and involuntary contraction of a muscle that becomes hard and difficult to relax. It can last from a few seconds to several minutes and often leaves the muscle sore afterward.
A muscle spasm is a broader term that refers to any involuntary muscle movement, which may or may not be painful. Spasms can feel like twitching, fluttering, or tightening, while cramps are usually intense and painful. In everyday use, people often use both terms interchangeably, but medically, cramps are a more severe type of spasm.
How long do muscle cramps usually last?
Most muscle cramps last a few seconds to several minutes, but the soreness and tightness can remain for several hours or even up to two days after the cramp stops.
If cramps last longer than 10–15 minutes, keep returning, or interfere with walking or sleeping, it may indicate dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or an underlying medical issue that needs evaluation.
Can dehydration alone really cause severe muscle cramps?
Yes. Dehydration is one of the most common and serious causes of muscle cramps, especially in hot climates like Las Vegas. When your body lacks enough fluids:
-
Blood becomes thicker and circulates more slowly
-
Muscles receive less oxygen and nutrients
-
Electrical signals between nerves and muscles become disrupted
This can lead to sudden and painful muscle contractions, particularly in the calves, thighs, feet, and hands. Even mild dehydration can increase cramp risk, especially during heat exposure or physical activity.
Which electrolytes are most important for preventing muscle cramps?
The key electrolytes that help muscles contract and relax properly include:
-
Potassium – regulates muscle and nerve signals
-
Sodium – maintains fluid balance and nerve function
-
Calcium – needed for muscle contraction
-
Magnesium – helps muscles relax after contraction
Low levels of any of these can cause irregular muscle firing and cramping. Electrolyte loss often happens with heavy sweating, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive alcohol use, or poor nutrition.
Are nighttime leg cramps a sign of poor circulation?
They can be. Nighttime leg cramps may be caused by:
-
Reduced blood flow during prolonged lying or sitting
-
Tight muscles or poor flexibility
-
Dehydration or electrolyte loss
-
Vascular conditions that limit circulation
If leg cramps happen frequently at night or are accompanied by leg pain during walking, numbness, or cold feet, poor circulation may be a contributing factor and should be medically evaluated.
When should muscle cramps be considered a medical emergency?
You should seek urgent medical care if muscle cramps:
-
Are severe or persistent
-
Occur without physical activity or heat exposure
-
Are accompanied by swelling, redness, weakness, numbness, confusion, or chest pain
-
Follow vomiting, diarrhea, or illness
-
Do not improve with fluids, stretching, and rest
These symptoms may indicate serious dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, nerve problems, or circulation disorders that require medical treatment.
Can medications trigger muscle cramps?
Yes. Several medications can increase the risk of cramps by affecting fluids, electrolytes, or muscle tissue, including:
-
Diuretics (water pills) that increase fluid loss
-
Statins that may affect muscle fibers
-
Blood pressure medications that alter circulation
-
Some asthma and psychiatric medications
If cramps begin soon after starting a new medication, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider rather than stopping the medicine on your own.
Why are muscle cramps more common in Las Vegas?
Las Vegas has a hot and very dry desert climate, which increases the risk of:
-
Rapid dehydration
-
Excessive sweating
-
Faster electrolyte loss
People may not feel how much fluid they are losing because sweat evaporates quickly in dry air. Outdoor work, exercise, alcohol use, and long hours in the heat all increase the likelihood of muscle cramps in this environment.
Can urgent care treat muscle cramps effectively?
Yes. Urgent care centers can evaluate the underlying cause of muscle cramps and provide treatments such as:
-
IV fluids for dehydration
-
Electrolyte replacement therapy
-
Pain management if needed
-
Evaluation for underlying medical conditions
Many patients experience rapid symptom relief after IV hydration and electrolyte correction, especially when cramps are caused by heat or fluid loss.
How can I prevent muscle cramps from coming back?
To reduce future muscle cramps:
-
Drink water consistently throughout the day
-
Use electrolyte drinks during heavy sweating or exercise
-
Stretch before and after physical activity
-
Avoid sitting or standing in one position for too long
-
Maintain a balanced diet with minerals
-
Limit alcohol intake, especially in hot weather
People with medical conditions should also follow treatment plans and attend regular checkups to reduce cramp risk.
Are frequent muscle cramps a sign of an underlying disease?
They can be. Frequent or worsening muscle cramps may be associated with:
-
Diabetes-related nerve damage
-
Kidney disease affecting electrolyte balance
-
Thyroid disorders
-
Nerve compression or spinal conditions
If cramps are happening regularly without clear triggers, medical evaluation is important to rule out systemic conditions.